As the legalization and therapeutic application of cannabis continue to expand globally, medical researchers and consumers alike are increasingly scrutinizing its side effects. While cannabis is frequently utilized for managing chronic pain, nausea, and anxiety, a growing number of anecdotal reports and clinical observations have raised a significant question: can cannabis cause tinnitus? Tinnitus, characterized by a persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound in the ears without an external source, affects millions of individuals worldwide. The relationship between cannabis consumption and auditory perception is rooted in the complex interactions between cannabinoids and the central nervous system. Specifically, the presence of cannabinoid receptors within the auditory brainstem suggests that the plant’s active compounds may directly influence how sound is processed and interpreted. While some users seek cannabis to alleviate the distress associated with pre-existing tinnitus, others report the onset of auditory phantom sounds following consumption. Understanding this dichotomy requires a deep dive into the endocannabinoid system’s role in sensory processing and the varying effects of different cannabis constituents on neural hyperactivity.
Can Cannabis Cause Tinnitus? Exploring the Link Between Cannabinoids and Auditory Perception
The Endocannabinoid System and Auditory Processing
To understand whether can cannabis cause tinnitus, one must first examine the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is a vast regulatory network comprising receptors (CB1 and CB2), endocannabinoids, and enzymes that maintain homeostasis. Research has confirmed that CB1 receptors are highly concentrated in the cochlear nucleus, the primary site in the brainstem where auditory nerve fibers terminate.
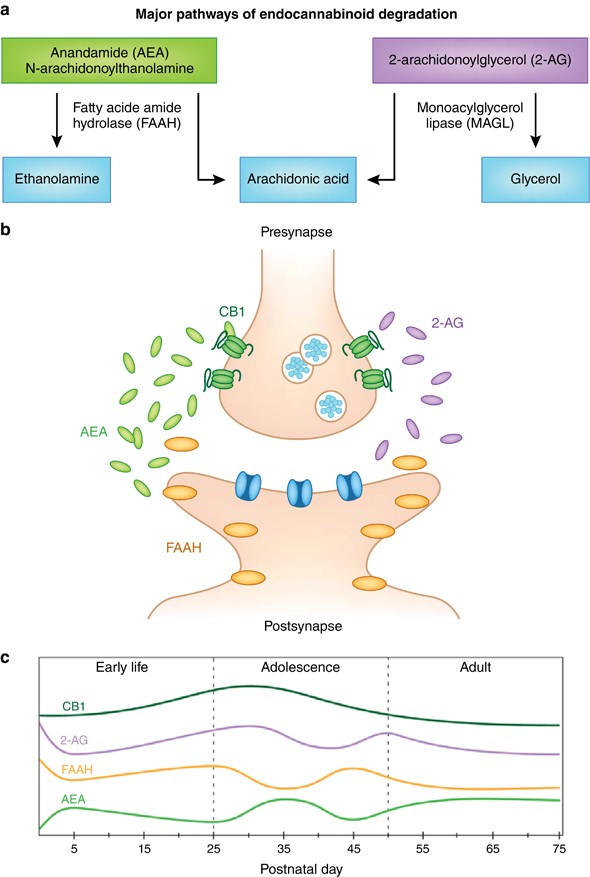
The cochlear nucleus plays a critical role in filtering and prioritizing sound signals before they reach the auditory cortex. When exogenous cannabinoids like THC bind to these receptors, they can alter the balance of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. This disruption may lead to neural hyperactivity within the auditory pathway, which is a hallmark of tinnitus. Rather than masking the sound, cannabis may inadvertently “turn up the volume” on internal neural noise.
Scientific Research: Can Cannabis Cause Tinnitus?
Current clinical evidence regarding cannabis-induced tinnitus is multifaceted. Some studies suggest that the psychoactive nature of cannabis, specifically through THC, enhances sensory awareness and can exacerbate the perception of pre-existing tinnitus. A significant study published in Frontiers in Neurology indicated that cannabinoids may promote the development of tinnitus in certain animal models, particularly after noise-induced hearing loss.
The Mechanism of Neural Hyperactivity
The prevailing theory among otolaryngologists is that tinnitus results from a lack of “sensory gating.” When the brain loses input from the ears—due to age or loud noise—it compensates by increasing the sensitivity of auditory neurons. THC may further stimulate these hypersensitive neurons, potentially triggering or worsening the sensation of ringing. This suggests that the impact of cannabis is not ototoxic (damaging to the ear itself) but rather neurological in nature.
Acute vs. Chronic Effects
The duration of cannabis-related tinnitus often depends on the frequency of use. Acute episodes may occur during intoxication, where the heightened sensory state makes a user more aware of internal sounds. Chronic use, however, may lead to long-term changes in receptor density in the brainstem, potentially leading to persistent auditory symptoms even after cessation of use.
Comparative Effects: THC versus CBD
Not all cannabinoids affect the auditory system in the same manner. The two most prominent compounds, Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD), exhibit contrasting profiles regarding auditory perception and neural excitation.
| Feature | THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) | CBD (Cannabidiol) |
|---|---|---|
| Receptor Interaction | Direct CB1 Agonist | Indirect Antagonist/Modulator |
| Effect on Auditory Nerves | Potential for hyperactivity | Potential for neuroprotection |
| Tinnitus Risk | Higher (dose-dependent) | Low to Negligible |
| Psychoactive Impact | High (increases sensory focus) | None (may reduce anxiety) |
Factors Influencing Auditory Sensitivity
The likelihood of experiencing tinnitus from cannabis is influenced by several biological and environmental variables. Individuals with a history of hearing loss or those predisposed to anxiety may be more susceptible to the auditory side effects of high-THC strains. Furthermore, the method of consumption can impact the intensity and onset of symptoms.
| Variable | Description of Impact |
|---|---|
| Dosage | Higher concentrations of THC are more likely to trigger neural hyperactivity. |
| Pre-existing Conditions | Individuals with existing hearing damage are at a higher risk of exacerbation. |
| Strain Profile | Sativa strains with high terpene counts may increase heart rate and sensory awareness. |
| Psychological State | Anxiety and hyper-focus can amplify the subjective distress of tinnitus. |
Key Takeaways
- CB1 receptors in the auditory brainstem are directly influenced by cannabinoids.
- THC is more likely than CBD to exacerbate or cause tinnitus due to its excitatory effects on neural pathways.
- The relationship between cannabis and tinnitus is often dose-dependent, with higher doses posing a greater risk.
- While cannabis is not traditionally considered ototoxic, it can alter sensory gating and increase auditory awareness.
- Individuals already suffering from tinnitus should exercise caution when using high-THC products.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does cannabis-induced tinnitus go away?
In most acute cases, the ringing subsides as the cannabinoids are metabolized and cleared from the system. However, for chronic users, it may take several weeks of abstinence for the auditory system to return to its baseline state. If the tinnitus persists beyond the period of intoxication, it is advisable to consult an audiologist to rule out underlying hearing loss.
Can CBD oil help treat existing tinnitus?
Currently, there is no definitive clinical evidence that CBD cures tinnitus. While CBD may help manage the stress, anxiety, or sleep disturbances associated with the condition, it does not appear to eliminate the phantom sounds themselves. Some users find relief through CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties, but results vary significantly between individuals.
Why does the ringing get louder after I smoke?
The psychoactive effects of THC can lead to a phenomenon known as “sensory enhancement,” where the brain becomes hyper-aware of internal stimuli. Additionally, THC can increase blood pressure and heart rate, which in some cases of pulsatile tinnitus, can make the internal sounds appear louder or more rhythmic.
Is there a specific strain that won’t cause ringing?
While no specific strain can be guaranteed to prevent tinnitus, products with a high CBD-to-THC ratio are generally less likely to cause sensory disturbances. Avoiding high-potency concentrates, such as dabs or high-percentage edibles, may also reduce the risk of triggering an auditory reaction.